Cloud Security Tips for HR Teams to Protect Employee Data in 2026
HR teams handle one of the most confidential information in any organization: personally identifiable information (PII), payroll data, performance analysis, health data, and even biometrics data. As HR management systems (HRMS) are shifted to be cloud-based, cloud security tips cease to be optional; it is necessary to protect the information about employees, prevent expensive breaches, and retain the trust.
In 2026, cyber threats evolve rapidly, making proactive protection critical.

Why Cloud Security Tips Are More Critical Than Ever for HR Teams?
Cybercriminals find employee information very useful to steal identity, commit fraud, or ransomware. According to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) reported over 3,300 data breaches in the US in 2024 and they involved over 1.6 billion people. In the meantime, the 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report published by Verizon concluded that in approximately 68% of the breaches, human factors had a role to play. The threat to cloud environments is growing due to AI-based security risks such as deepfakes phishing attacks on HR personnel, vulnerabilities in the supply chain, and insider mistakes.
The pressure on regulation is also increasing: GDPR enforcement in the EU is still high, and regulations such as the Data Protection Act 2079 (2023) in Nepal require it, and schemes, such as SEC breach notification guidelines, provide a sense of urgency. One violation will result in millions of fines, litigation, lost reputation, and lack of trust among the employees, which will affect retention and morale. Strong cloud security tips reduce these risks, ensure compliance, and reinforce the ethical handling of HR data, demonstrating that HR prioritizes employee data protection.
Top Cloud Security Risks Facing HR Software in 2026
HRMS systems have long-standing and new-comer threats:
- Unauthorized access through credential stuffing or phishing
- Misconfigured cloud settings, like public storage buckets or overly permissive IAM roles
- Insider threats and human error, contributing to 60–68% of incidents
- Third-party or supply-chain vulnerabilities in integrations or vendors
- Ransomware attacks on payroll and HR systems
- AI-enhanced threats, including deepfakes for social engineering
These challenges underscore the need for layered cloud security defenses.
Real Companies. Real Breaches. Real Consequences
These aren’t hypothetical scenarios. They occurred during the past 12 months:
Case 1: Volvo (August 2025)
- What happened: Third-party HR provider Miljödata got hit with ransomware
- What was stolen: Employee names, SSNs, addresses, birth dates
- The lesson: Your vendor’s security problem becomes YOUR security problem
Case 2: ManpowerGroup (Late 2024/Early 2025)
- What happened: RansomHub ransomware attack
- Impact: 144,000-145,000 people’s data leaked
- What was exposed: Payroll data, SSNs, passport numbers, contact details
- The lesson: No backups? You’re at the mercy of hackers
Case 3: Workday (August 2025)
- What happened: Third-party CRM Social engineering attack
- Attack method: Hackers posed as HR and IT employees
- The lesson: Manipulation by man is not over Train your people.
Notice the pattern?
Supply chain attacks + human manipulation = most breaches in 2026.
Top 10 Cloud Security Tips for HR Teams in 2026
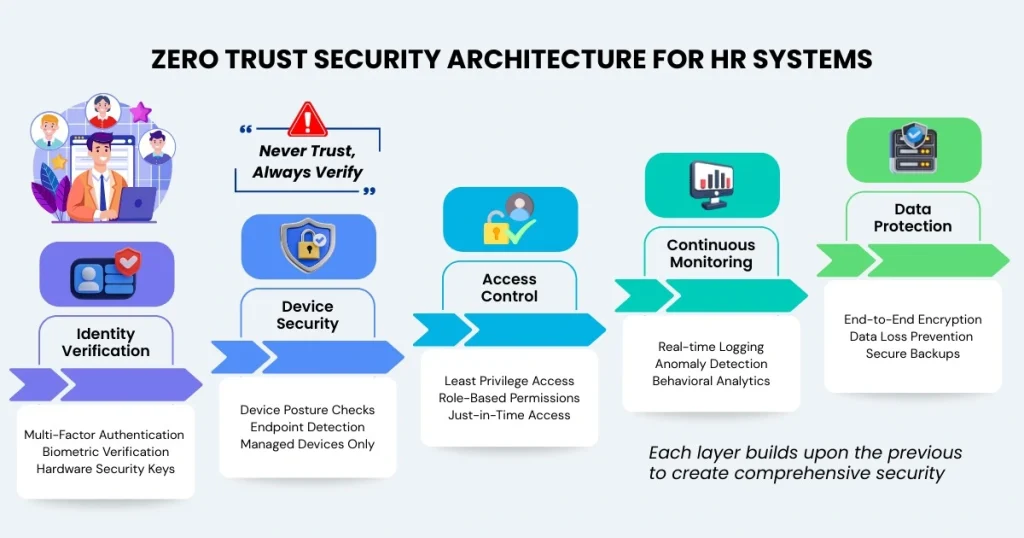
Adopt Zero Trust Principles for HR Access Control
Always verify implementation Use never, and always verify implementation with constant authentication, role based access control (RBAC) and least privileged, just in time permissions and posture checks on devices in hybrid workflows.
Mandate Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Introduce MFA (hardware keys and biometrics) which is phishing resistant on all HR accruals. 99.9% of account compromise attacks are blocked by MFA.
Encrypt All Employee Data
Encrypt all employee data at rest using AES-256 and data in transit using TLS 1.3+. Encrypt backups and third-party shares, and obsolete protocols such as TLS 1.0/1.1.
Continuous Cloud Monitoring & Anomaly Detection
Logins, access, and downloads should be enabled to be logged in real-time. Detect abnormal patterns and massive data migrations through the help of artificial intelligence.
Automated Backups & Disaster Recovery Plans
Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule with immutable backups. Regularly (not more than once every quarter) perform test restore procedures.
Secure Configurations, Patches & Vendor Management
Misconfigurations should be scanned, patching should be done automatically and third-party audits should be carried out comprehensively. Make certain that vendors adhere to your security levels.
HR-Focused Security Training
Just in Time phishing simulation and staff security education on how to handle securely payroll information, remote onboarding with secure devices, and reporting suspicious activity.
Data Residency Compliance
Ensure your HRMS provider offers regional hosting options that comply with Nepal’s Data Protection Act and international regulations.
Respect Employee Privacy Rights
Respond to data subject access request in accordance with the instant and educate HR personnel on how to amend, remove, or export employee information as necessary.
AI Usage Governance in HR
Ensure AI tools for resume screening or performance analytics comply with data protection rules, retain minimal employee data, and are transparent.
Develop an HR-Specific Incident Response Plan
Your plan should include:
- Clear roles for HR, IT, legal, and communications
- Templates for employee and regulator notifications
- Timelines per breach notification laws (e.g., GDPR within 72 hours)
- Forensic investigation procedures
- Post-incident review and improvement exercises
A strong incident response plan should align with your internal communication strategy to ensure employees receive clear, timely, and accurate updates during a breach.
Common Cloud Security Mistakes HR Teams Still Make
- Over-provisioning admin access
- Not attending MFA or applying feeble techniques
- Contravention of security logs and anomalies
- The naivety of cloud vendors
- Failure to undertake auditing of the third-party vendors
- Lax controls on remote or hybrid access
Cloud Security Tips Checklist for HR Teams (2026 Edition)
- Turn on phishing resistant MFA
- Use Zero trust + least privilege access
- Encrypt data at rest, data in transit and back-up
- Constant surveillance and AI anomaly detection
- Holding secure backups and quarterly test restores
- Carry out HR-related phishing exercises
- Conduct audit of third parties vendors on an annual basis
- Prepare HR response strategy/plan
How These Cloud Security Tips Protect Employee Data & Build Trust?
It should take the following steps:
- Lowers probability and impact of breaches
- Ensures regulatory compliance
- Helps avoid substantial fines
- Fosters employee trust in HR processes
Using secure tools like HajirHR’s performance management and employee self-service software further strengthens HR operations.
Choosing Secure HR Software: Key Features HR Teams Need
With regard to cloud HR solutions, there are:
- Built-in Zero Trust and identity management
- End-to-end encryption, audit logs, real-time monitoring
- AI-driven threat detection
- Automated compliance reporting
- Transparent supply-chain security
- Regional hosting for data residency
- Disaster recovery and business continuity features
HajirHR offers all of these features, ensuring secure cloud HR platform management for attendance, payroll, and HR tasks while remaining compliant with Nepal and international standards.
Final Thoughts
The process of cloud security is a continuum, and not a single exercise. The HR teams should work closely with IT, keep abreast of the emerging threats, select safe HR software, and keep a sustained vigilance.
By following these cloud security tips, HR can effectively protect employee data, comply with regulations, and foster a secure, trustworthy workplace in 2026 and beyond.
FAQ
Start with the Big 3: (1) Phishing-resistant MFA on every account, (2) AES-256 encryption for all employee data, and (3) Monthly security training with phishing simulations. Then add Zero Trust access controls, real-time monitoring, and the 3-2-1 backup rule. These six measures will protect you against 90%+ of common attacks.
The fatal six: (1) Giving too many people admin access, (2) Using weak MFA like SMS codes, (3) Never checking security logs, (4) Assuming your cloud provider handles everything, (5) Not vetting third-party vendors, and (6) Allowing unsafe remote work practices. Each one can be a backdoor for hackers.
Follow your incident response plan: (1) Contain the breach immediately:disconnect compromised systems, (2) Assess scope:what was accessed?, (3) Notify your incident response team and legal counsel, (4) Document everything for forensics, (5) Notify regulators within 72 hours (GDPR requirement), and (6) Communicate transparently with affected employees. Speed matters, every hour counts.
There are, of course, any number of other security risks and cloud security threats: denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, malware, phishing, data leakage, cloud vendor security risk, unauthorised access, insider threats, limited visibility of network systems and many more.
The Four A'sZ: Administration, Authentication, Authorization, and Audit: aren't just technical processes. They reflect the shift from securing places to securing people. In today's world, where users and data are everywhere, IAM isn't optional. It's the foundation of security.



